![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
= 0 .
It follows that
![]() or 4x+3 = 0 .
or 4x+3 = 0 .
Thus, the values of x which solve f'(x) = 0 are
![]() or
or ![]() .
.
Click HERE to return to the list of problems.
SOLUTION 14 : Consider the function ![]() . For what values of x is f'(x)=0 ? Begin by differentiating the function using the product rule. Then
. For what values of x is f'(x)=0 ? Begin by differentiating the function using the product rule. Then
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
= 0 .
It follows that
![]() or -x+1 = 0 .
or -x+1 = 0 .
But ![]() can never be zero since an exponential is always positive.
Thus, the only values of x which solve f'(x) = 0 are
can never be zero since an exponential is always positive.
Thus, the only values of x which solve f'(x) = 0 are
x = 0 or x = 1 .
Click HERE to return to the list of problems.
SOLUTION 15 : Consider the function ![]() . For what values of x is f'(x)=0 ? Begin by differentiating the function using the product rule. Then
. For what values of x is f'(x)=0 ? Begin by differentiating the function using the product rule. Then
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
= 0 .
It follows that
x = 0 or ![]() .
.
But x = 0 is not in the domain of function f since ![]() is not defined.
Thus, the only possibility is
is not defined.
Thus, the only possibility is
![]()
iff
![]()
iff
![]()
iff
![]()
iff
![]() .
.
Click HERE to return to the list of problems.
SOLUTION 16 : Prove that
![]() .
.
Group functions f and g and apply the ordinary product rule twice. Then
![]()
![]()
![]()
= f'(x) g(x) h(x) + f(x) g'(x) h(x) + f(x) g(x) h'(x) .
Here is an easy way to remember the triple product rule. Each time differentiate a different function in the product. Then add the three new products together.
Click HERE to return to the list of problems.
SOLUTION 17 : Differentiate ![]() . Differentiate y using the triple product rule. Then
. Differentiate y using the triple product rule. Then
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Click HERE to return to the list of problems.
SOLUTION 18 : Consider the function ![]() . For what values of x is f'(x)=0 ? Begin by differentiating f using the triple product rule. Then
. For what values of x is f'(x)=0 ? Begin by differentiating f using the triple product rule. Then
![]()
![]()
(Now factor out the common terms of ![]() , and
, and ![]() .)
.)
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
It follows that
![]() or
or ![]() .
.
But ![]() is never zero since exponentials are always positive. Thus, the values of x which solve f'(x)=0 are
is never zero since exponentials are always positive. Thus, the values of x which solve f'(x)=0 are
![]() or (using the quadratic formula)
or (using the quadratic formula)
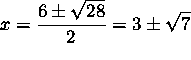 .
.
Click HERE to return to the list of problems.
SOLUTION 19 : Find an equation of the line tangent to the graph of
![]() at
at ![]() . If
. If ![]() then
then
![]() so that the tangent line passes through the point
so that the tangent line passes through the point
![]() . The slope of the tangent line follows from the derivative of y . Then
. The slope of the tangent line follows from the derivative of y . Then
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
The slope of the line tangent to the graph at ![]() is
is
![]() .
.
Thus, an equation of the tangent line is
![]() or y=x .
or y=x .
Click HERE to return to the list of problems.
SOLUTION 20 : Find an equation of the line perpendicular to the graph of
![]() at
at ![]() . If
. If ![]() then
then
![]() so that the tangent line
passes through the point
so that the tangent line
passes through the point ![]() . The slope of the line perpendicular to
the graph of f will be perpendicular to the line tangent to the graph of f . Thus, we need to first
compute the derivative of f . Then
. The slope of the line perpendicular to
the graph of f will be perpendicular to the line tangent to the graph of f . Thus, we need to first
compute the derivative of f . Then
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Thus, the slope of the line tangent to the graph at ![]() is
is
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Thus, the slope of the line perpendicular to the graph at ![]() is
is
![]()
and an equation of this line is
![]() .
.
Click HERE to return to the list of problems.
SOLUTION 21 : Find all points (x, y) on the graph of ![]() with tangent lines parallel to the line y + x = 12 . The slope of the given line y = 12-x is y'=-1 . Thus, we need to find all values x in the domain of f which satisfy f'(x)=-1 . The derivative of f is
with tangent lines parallel to the line y + x = 12 . The slope of the given line y = 12-x is y'=-1 . Thus, we need to find all values x in the domain of f which satisfy f'(x)=-1 . The derivative of f is
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
If ![]() then
then ![]() . It follows that
. It follows that
![]()
iff
![]()
iff
![]()
iff
![]()
iff
x(9x + 8) = 0 .
Thus,
x = 0 or 9x + 8 = 0
so that
x = 0 or ![]() .
.
But x=0 cannot be a solution since ![]() . Therefore, the only solution is the point
. Therefore, the only solution is the point
![]()
and
![]() .
.
Click HERE to return to the list of problems.